Diagnostics is a field which helps in confirming a provisionally diagnosed disease. This is carried out using various modalities. These include the following:
a) Clinical Laboratory
Here haematological, chemical, immunological, microbiological and other advanced tests are performed on blood, urine, stool, surgical specimens collected during surgeries, and any other body fluid or tissue.
b) Radiology or X-Rays
Here routine X-rays of various parts of the body are conducted to diagnose the problem.
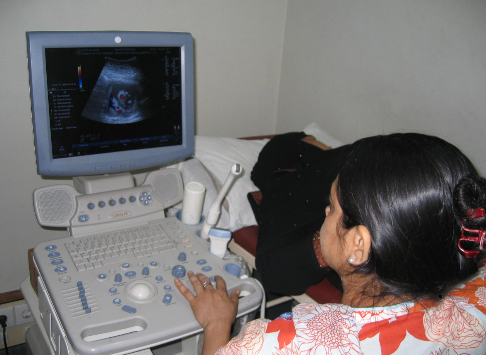
c) Ultrasound scanning
Ultrasound scanning is mainly used in obstetrics and assessment of various soft organs of the body. Common tests include evaluation of baby in pregnant mothers, assessment of organs in abdomen, determining functions of heart (Echocardiography).
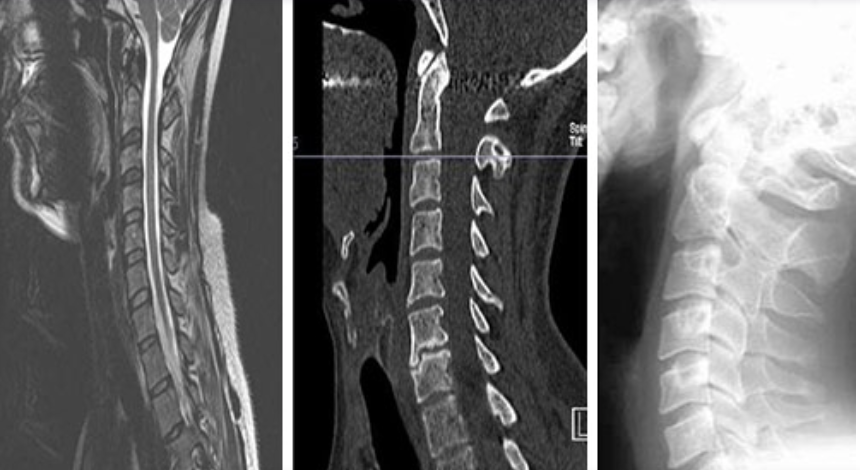
d) CT-Scanning (CT Scan)
It is a computer-assisted special type of X-ray which is more sensitive than ordinary X-rays. It is advised by a consultant where indicated.
e) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
It is another form of computer-assisted special type of scanning without using X-rays. It is safe and more sensitive. It is advised by a consultant where indicated.